TITLE
Chrysotila pseudoroscoffensis as a source of high-value polar lipids with antioxidant activity: A lipidomic approach
JOURNAL
Algal Research
AUTHORS
Ana S. P. Moreira, Joana Gonçalves, Tiago A. Conde, Daniela Couto, Tânia Melo, Inês B. Maia, Hugo Pereira, Joana Silva, M. Rosário Domingues, Cláudia Nunes
ABSTRACT
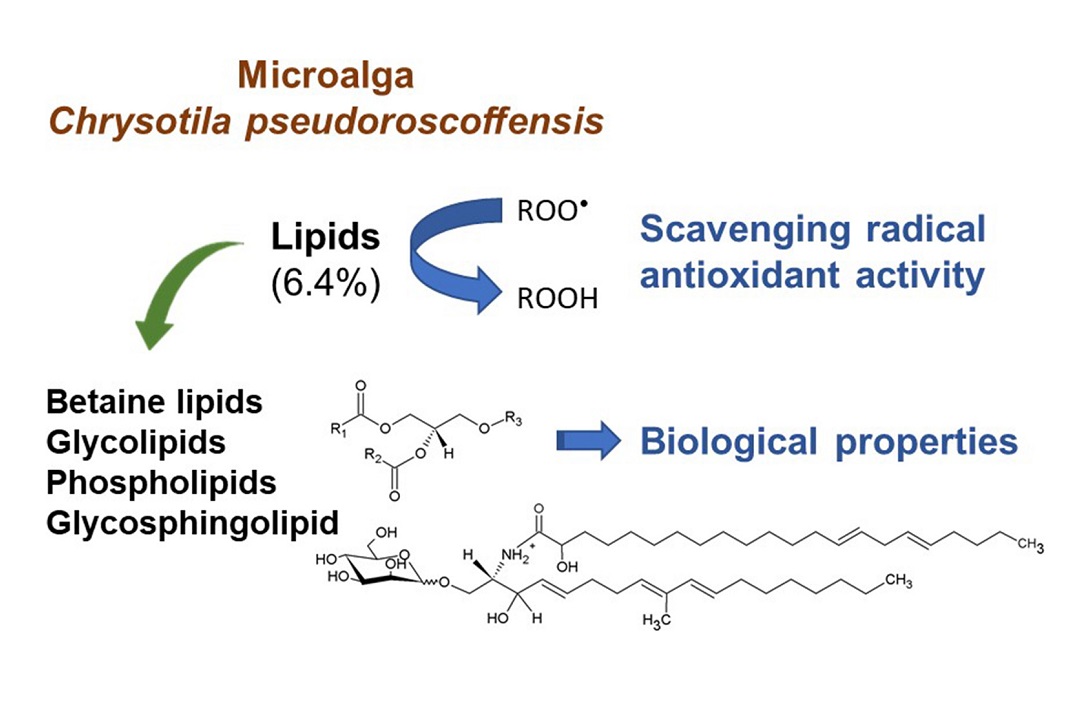
Microalgae are emerging as sustainable sources of a wide range of high-value compounds. However, the knowledge about microalgae polar lipids is still limited, despite their interest due to their chemical diversity and bioactivity. This study shows, for the first time, the polar lipidome of the haptophyte microalga Chrysotila pseudoroscoffensis unveiled by using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (HILIC-HRMS and MS/MS) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Freeze-dried C. pseudoroscoffensis biomass has a lipid content of 6.4 %, containing higher amounts of ash (45.5 %), proteins (11.6 %), and sugars (11.0 %). Uronic acids (53.8 mol%) are the sugars present in higher content, followed by glucose (13.7 mol%) and galactose (12.7 mol%). The polar lipid species identified by HILIC-MS/MS included betaine lipids, glycolipids, and phospholipids, some of them with recognised bioactive properties. Among the lipid classes found from C. pseudoroscoffensis, some are less reported in algae: betaine lipids diacylglycerylcarboxyhydroxymethylcholine (DGCC) and monoacylglycerylcarboxyhydroxymethylcholine (MGCC) (characteristic of haptophyte microalgae); acid glycolipid class glucuronosyldiacylglycerol (GlcADG) (mainly reported in plants with protective effects in phosphate-deprivation conditions); and phospholipid classes monomethylphosphatidylethanolamine (MMPE) and lysomonomethylphosphatidylethanolamine (MMLPE). As estimated by colorimetric assays, glycolipids and phospholipids accounted for 64 and 3 % of the total lipid extracts, respectively. Fatty acid profiling by GC–MS showed that total esterified fatty acids accounted for about 32 % of the total lipid extracts, of which 23 % were omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). Four lipid extract concentrations (12.5, 62.5, 125 and 250 μg mL−1 in ethanol) were tested and displayed antioxidant capacity toward 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals. A dose-dependent behaviour was observed with IC50 of 111.9 μg mL−1 for ABTS and IC35 of 234.8 μg mL−1 for DPPH assay. In conclusion, the lipid extracts of C. pseudoroscoffensis may be a source of high-value lipids for the development of novel microalgae-based products, namely nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals.



