TITLE
Clean production of microalgae high-value lipid fraction: Influence of different pretreatments on chemical and cytotoxic profiles of Chlorella vulgaris supercritical extracts and life cycle assessment
JOURNAL
Journal of Cleaner Production
AUTHORS
Jelena Valdic, Sanja Radman, Zeljko Zizac, Irina Besu, Igor Jerkovic, Lais Galileu Speranza, Ahmad Furgan Hala, Strahinja Kovacevic, Hugo Pereira, Luisa Gouveia
ABSTRACT
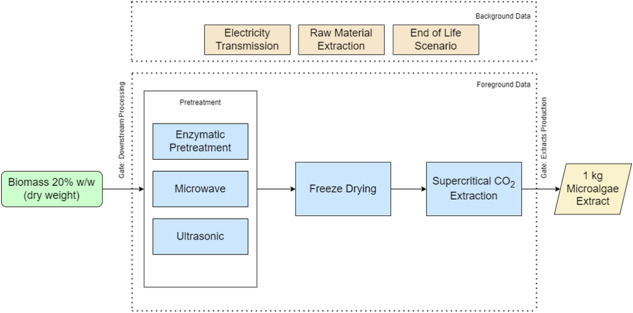
Microalgae have emerged as a promising natural resource rich in bioactive compounds. Health-beneficial properties of microalgae, coupled with advantageous characteristics such as high biomass productivity, adaptability, robustness, and carbon dioxide mitigation, position them as a viable solution for global sustainable food production. This study explored clean and environmentally friendly processes to enhance the recovery of lipid bioactive fractions. Microwave (MW), enzymatic (ENZ), and ultrasound (US) pretreatments were applied to improve environmentally friendly extraction of lipid-based components using supercritical CO2. The effects of these pretreatments on extraction yield, chemical profiles, and cytotoxic properties of Chlorella vulgaris (Cv) and smooth C. vulgaris (sCv) extracts were investigated. Additionally, a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) was conducted to evaluate environmental impacts. MW pretreatment achieved the highest yield increases, from 2.58 times (Cv) to 3.15 times (sCv). UHPLC-ESI-HRMS analysis revealed shifts in the distribution of pigments and derivatives caused by pretreatments, with ENZ extracts showing the most pronounced changes: pigments increased from 9.24% (control Cv) to 40.92% (Cv) and from 12.52% (control sCv) to 71.12% (sCv). Cv extracts exhibited greater activity against MDA-MB-453 cells, while sCv extracts from US pretreatment demonstrated the strongest effect on HeLa cells. The LCA indicated reduced environmental impacts of the pretreatment-enhanced processes up to 65% compared to the control. A scenario analysis was presented to show further possible impact reduction by recirculating the CO2 solvent and substituting the energy source. These findings provide valuable insights into sustainable and scalable green processes for recovering microalgal bioactive components.



